Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Guide to Change Thought Patterns
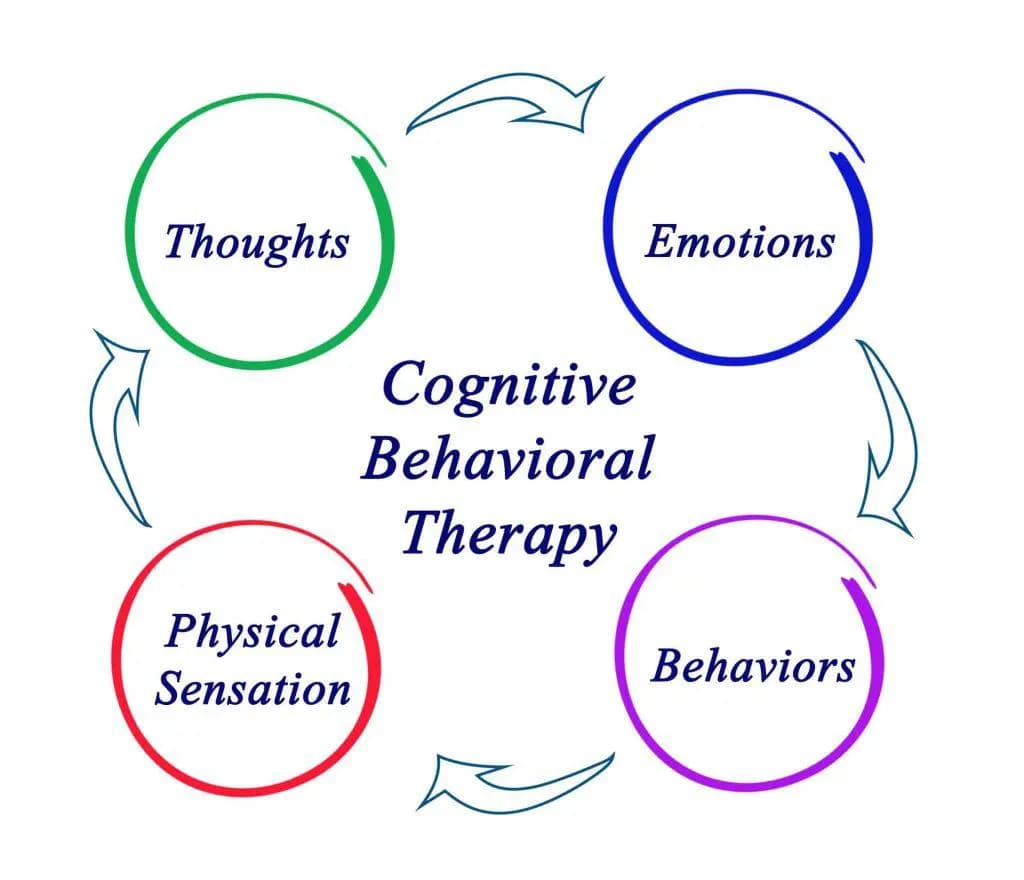
In the contemporary tapestry of our fast-paced lives, where stress and anxiety have woven themselves into the fabric of everyday existence, the imperative of prioritizing mental health has never been more apparent. Navigating the intricate labyrinth of our thoughts and emotions requires a profound understanding, and it is within this context that Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) emerges as a beacon of hope and transformation. Welcome to "Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Guide to Change Thought Patterns," a comprehensive exploration that transcends the surface, delving into the profound principles, tangible benefits, and the revolutionary impact Careme Health is making in reshaping mental health support in the vibrant landscape of India.
This guide is more than just a compilation of information; it is a companion on your journey to understanding and implementing change in the very fabric of your thoughts. So, let's embark on this transformative exploration together, navigating the maze of our minds and emerging on the other side with newfound insights and the tools to change thought patterns for a brighter, more resilient mental outlook.
Unraveling the Tapestry of Change: The Evolution and Essence of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) has a fascinating history, shaped by the contributions of several pioneers in the field. Let's take a brief journey through time to understand how CBT evolved into the transformative therapy it is today.
Origins in Behavior Therapy (1920s-1950s): The roots of CBT can be traced back to behavior therapy, which focused on understanding and modifying observable behaviors. During the 1920s to 1950s, behaviorists like John B. Watson and B.F. Skinner laid the groundwork by emphasizing the importance of studying behaviors as a way to comprehend and address psychological issues.
Cognitive Therapy Emerges (1960s): In the 1960s, Dr. Aaron Beck, a psychiatrist, introduced cognitive therapy as a response to the limitations of behavior therapy. Dr. Beck observed that individuals experiencing depression often had distorted and negative thought patterns. His groundbreaking work emphasized the role of cognition in shaping emotions and behavior.
Integration of Cognitive and Behavioral Approaches (1970s): The 1970s marked a pivotal period when cognitive and behavioral approaches started to merge. Dr. Albert Ellis, another influential figure, developed Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), which highlighted the connection between irrational thoughts and emotional distress. This integration laid the foundation for what would later be known as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy.
Formalization of CBT (1980s-1990s): During the 1980s and 1990s, CBT gained recognition as a distinct therapeutic approach. Dr. Judith Beck, the daughter of Aaron Beck, contributed to the formalization of CBT methods. The approach became increasingly structured, incorporating systematic techniques to identify and modify maladaptive thoughts and behaviors.
In the 2000s, CBT achieved widespread acceptance and became one of the most researched and practiced forms of psychotherapy. Therapists worldwide began integrating CBT principles into the treatment of various mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and stress. Today, CBT stands as a cornerstone in mental health treatment, offering individuals practical tools to understand and change their thought patterns.
Unraveling the Science of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Journey into Transformative Change
The science behind Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is grounded in rigorous research and has demonstrated its effectiveness in transforming thought patterns and improving mental health. Let's explore the key aspects of the science behind CBT in a simplified manner:
- Cognitive Restructuring:
- Explanation: CBT focuses on cognitive restructuring, which involves identifying and challenging negative thought patterns.
- Research Insight: Numerous studies have shown that modifying distorted thoughts positively impacts emotions and behaviors (Beck, 1963).
- Behavioral Activation:
- Explanation: CBT encourages positive actions through behavioral activation, fostering a proactive approach to life.
- Research Insight: Behavioral activation has been proven effective in treating depression by increasing engagement in meaningful activities (Dimidjian et al., 2006).
- Exposure Therapy:
- Explanation: Exposure therapy helps confront fears gradually, reducing anxiety over time.
- Research Insight: Research supports the efficacy of exposure therapy in treating various anxiety disorders, such as PTSD and phobias (Foa et al., 2007).
- Neuroplasticity and CBT:
- Explanation: CBT contributes to neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize and adapt.
- Research Insight: Neuroimaging studies suggest that CBT can lead to structural changes in the brain, enhancing adaptive thinking (Goldin et al., 2016).
- CBT for Diverse Mental Health Challenges:
- Explanation: CBT is versatile and effective across a range of mental health challenges.
- Research Insight: Meta-analyses consistently show the efficacy of CBT in treating anxiety, depression, and other disorders (Hofmann et al., 2012).
- Mindfulness in CBT:
- Explanation: Mindfulness, often integrated into CBT, involves being present in the moment.
- Research Insight: Mindfulness-based CBT has shown positive outcomes in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression (Hofmann et al., 2010).
Careme Health Integration:
This section illuminates how Careme Health harnesses the science of CBT. Through features like 24*7 coach support, access to psychiatrists and psychologists, and a supportive community, Careme Health leverages the transformative power of CBT to provide real-time, evidence-based mental health support.
Empowering Change: Who Can Benefit from Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a versatile therapeutic approach that can be applied to a wide range of patients or clients facing various challenges. This guide aims to shed light on the conditions and situations where CBT can be particularly beneficial, breaking down the information into simple language for better understanding.
- Anxiety and Stress: CBT is highly effective for individuals dealing with anxiety disorders and stress. By identifying and challenging negative thought patterns contributing to anxiety, CBT empowers individuals to develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce stress levels.
- Depression: For those grappling with depression, CBT provides a structured framework to address distorted thinking and negative self-perceptions. Through cognitive restructuring, individuals can reshape their thoughts, leading to improved mood and a more positive outlook.
- Phobias and Fears: CBT is instrumental in treating phobias and fears by employing exposure therapy. This gradual and systematic approach helps individuals confront and overcome irrational fears, fostering a sense of control and empowerment.
- Relationship Issues: In the realm of interpersonal relationships, CBT aids individuals in identifying and modifying maladaptive thought patterns that may contribute to relationship challenges. It fosters healthier communication and coping strategies.
- Sleep Disorders: CBT techniques, such as cognitive restructuring and behavioral interventions, are valuable tools for addressing sleep disorders. By targeting and changing disruptive thought patterns, individuals can improve their sleep quality and establish better sleep hygiene.
- Chronic Pain Management: CBT plays a role in managing chronic pain by addressing the psychological aspects of pain perception. It helps individuals develop coping skills, reduce pain-related anxiety, and improve overall functioning.
- Eating Disorders: In the context of eating disorders, CBT is effective in addressing distorted body image, unhealthy eating patterns, and negative self-perceptions. It promotes a healthier relationship with food and fosters self-esteem.
- Substance Abuse and Addiction: CBT is a valuable component of substance abuse treatment, helping individuals recognize and change the thought patterns contributing to addictive behaviors. It supports relapse prevention and addresses underlying issues.
- Trauma and PTSD: CBT is widely used in the treatment of trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It assists individuals in processing traumatic experiences, challenging distorted beliefs, and developing coping strategies.
- General Well-being and Personal Growth: Beyond specific mental health conditions, CBT can benefit individuals seeking personal growth and enhanced well-being. It equips individuals with skills to manage life's challenges, enhance resilience, and foster a positive mindset.
Transforming Minds, Changing Lives: Measuring the Impact of Understanding CBT on Thought Patterns
Embarking on the journey of understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is not just an intellectual exploration but a transformative experience that resonates in the very fabric of our thoughts and emotions. This section unravels the tangible outcomes and provides a roadmap to measure the effectiveness of embracing CBT in altering thought patterns for the better.
- Clarity of Thought: Outcome: Enhanced clarity and awareness of one's thoughts and their impact on emotions and behavior. Measurement: Regular self-reflection, journaling, and tracking instances where newfound awareness led to positive shifts in mindset.
- Improved Emotional Regulation: Outcome: Greater ability to manage and regulate emotions, leading to reduced stress and anxiety. Measurement: Monitoring emotional responses in challenging situations, noting instances of improved emotional resilience and coping mechanisms.
- Positive Behavior Change: Outcome: Implementation of healthier and more adaptive behaviors in response to identified thought patterns. Measurement: Observing and recording instances where consciously changing thought patterns led to positive shifts in behavior.
- Increased Problem-Solving Skills: Outcome: Development of effective problem-solving skills through a more rational and constructive thought process. Measurement: Tracking instances where applying CBT principles resulted in improved problem-solving and decision-making.
- Enhanced Interpersonal Relationships: Outcome: Improved communication and understanding in relationships, fostering healthier connections. Measurement: Recognizing and documenting instances where changed thought patterns positively impacted interactions with others.
- Overall Well-being: Outcome: A sense of overall well-being and improved mental health. Measurement: Regular self-assessment using tools like mood trackers and well-being assessments, noting trends in mental health improvements over time.
- Application Beyond Therapy: Outcome: Transferability of CBT skills into various aspects of life, beyond therapeutic sessions. Measurement: Identifying and celebrating instances where CBT principles were autonomously applied in daily challenges.
Mapping Your Mind: Exploring Common Assessments in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
These tools serve as navigational instruments, helping individuals and therapists chart a course towards understanding and transforming thought patterns. Let's explore some common assessments employed in CBT, demystifying their purpose and utility in simple language.
2.1 Self-Assessment Questionnaires: Picture these like friendly surveys designed to understand how you think and feel in various situations. Self-assessment questionnaires are straightforward tools where you answer questions about your thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. They're like snapshots of your mental landscape, helping both you and your therapist identify patterns that might be contributing to challenges like stress or anxiety.
2.2 Thought Records: Think of thought records as a diary for your mind. Here, you jot down situations that trigger certain thoughts, the feelings associated with those thoughts, and how you responded. It's like capturing the play-by-play of your mind's reactions. By examining these records, you and your therapist can spot patterns, challenge unhelpful thoughts, and work towards more positive responses.
2.3 Behavioral Experiments: No lab coats here – just practical, real-life experiments. In CBT, behavioral experiments involve trying out new behaviors to test and challenge existing beliefs. It's like being a detective in your own life, experimenting with different ways of thinking and acting to see what works best. These experiments, conducted with guidance, help reshape thought patterns and build resilience.
2.4 Anxiety and Depression Scales: Imagine a scale from 1 to 10, where 1 is feeling great, and 10 is not so great. Anxiety and depression scales are simple tools that help quantify how you're feeling. During therapy, these scales provide a quick snapshot of your emotional state. Tracking changes over time helps gauge progress and tailor interventions to address specific challenges.
2.5 Automatic Thought Worksheets: Automatic thoughts are like the pop-ups in your mind – quick, automatic responses to situations. Worksheets are tools to catch and examine these thoughts. By identifying and challenging automatic thoughts, you can gain insight into the underlying beliefs influencing your emotions. It's like shining a light on the thoughts that pass through your mind in the blink of an eye.
2.6 Goal Setting: Goals here are like roadmaps for change. Together with your therapist, you identify specific, achievable goals. These could be small steps towards challenging thought patterns or developing new coping strategies. Working towards these goals provides direction and a sense of accomplishment, fostering a positive shift in thought patterns.
Charting a New Path to Mental Well-being
As we draw the curtains on our exploration of "Understanding Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A Guide to Change Thought Patterns," it becomes evident that the journey to mental well-being is not a solitary endeavor but a collaborative odyssey. Through the lens of CBT, we've uncovered the transformative power of reshaping our thought patterns, offering a beacon of hope amidst the complexities of modern life.
In concluding our guide, let us reflect on the holistic approach that Careme Health embodies in fostering mental resilience. By seamlessly integrating features such as self-care, 24*7 coach support, access to psychiatrists and psychologists, a supportive community, assessments, mood trackers, and immediate evidence-based care, Careme Health emerges as a comprehensive ally in the pursuit of mental wellness.
As you embark on your own journey of change and growth, remember that immediate support is at your fingertips, grounded in evidence-based care. The holistic ecosystem provided by Careme Health extends beyond the pages of this guide, offering a tangible framework to implement the principles of CBT into your daily life.
In the spirit of transformation, the "Conclusion" serves as both a reflection and a call to action. It invites you to embrace the tools and insights gleaned from our exploration, fostering a proactive approach to mental well-being. With Careme Health as a steadfast companion on this journey, you are equipped not only to understand but to actively change thought patterns, paving the way for a brighter, more resilient mental landscape.
Related Articles

Understanding Depression: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Depression is a complex mental health condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is more than just a feeling of sadness; it is a persistent state of low mood and aversion to activity that can significantly impact one's quality of life.

Healing Through Grief: Understanding the Stages of Loss and How to Cope
Grief is an inevitable part of life, touching everyone at some point. It’s an emotional, physical, and psychological response to loss, whether that loss comes from the death of a loved one, the end of a relationship, losing a job, or missing out on opportunities. For many, grief is a solitary and isolating experience, leaving individuals overwhelmed, confused, and unsure of how to move forward.

Understanding the Different Types of Anxiety Disorders and Their Symptoms
Anxiety is a natural response to stress and is part of the human experience. It becomes a disorder when it interferes significantly with daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Anxiety disorders are among the most common mental health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people annually. This blog explores the types of anxiety disorders, their symptoms, history, science, and the tools available to manage them.

Understanding and Managing Social Anxiety: Tips for Teenagers
Social anxiety is more common than most people realize, especially among teenagers who are navigating the challenges of school, friendships, social media, and family expectations. For teens facing social anxiety, the pressures of school, social gatherings, and public situations can feel overwhelming, sometimes resulting in avoidance, negative self-talk, or a sense of isolation. In India, as well as globally, social anxiety has seen an uptick, partly fueled by social media and academic pressures. Understanding and managing social anxiety is crucial for building confidence and enjoying life’s opportunities. Here’s an in-depth look at what social anxiety is, why it’s particularly prevalent during teenage years, and how to address it effectively.

The Science of Happiness: Understanding Mental Health and How to Cultivate Joy
In a world that seems to be constantly demanding more from us, the quest for happiness has become more pressing than ever. But what does science tell us about happiness? Is it merely the absence of sadness, or is there something deeper and more profound about cultivating joy? In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the scientific understanding of happiness, how it impacts mental health, and what actionable steps you can take to bring more joy into your life.

Breaking the Silence: Understanding Depression in Young Students
Depression among young students is a growing concern, yet it often goes unnoticed or misunderstood. The academic pressures, social struggles, and rapid changes that characterize youth can contribute to a decline in mental health, sometimes resulting in depression. This mental health condition not only hampers a student's academic performance but also affects their social interactions, self-esteem, and overall well-being. Understanding depression in young students is essential for parents, teachers, and caregivers to provide timely support.
